Phillips Carbon Black Limited (PCBL), a part of RP-Sanjiv Goenka Group, was set up by Mr. K. P. Goenka in 1960, with the core objective of substitution of the import of carbon black. The company started production at Durgapur with a production capacity of 14,000 MT per annum. As PCBL celebrated its diamond jubilee in 2020, it has been playing a pioneering role in the carbon black industry for many years.
Today, PCBL is the largest carbon black manufacturer in India and a strong global player with a significant customer base in various countries. Apart from four strategically located state-of-the-art plants at Durgapur (West Bengal), Palej (Gujarat), Mundra (Gujarat) and Kochi (Kerala), it has also set up R&D centres at Palej (Gujarat) and Belgium.
Business area of the company
The Company is primarily engaged in the business of manufacturing & sale of carbon black and sale of power.
Rubber Black, Specialty Black and Power are the primary products of the company.
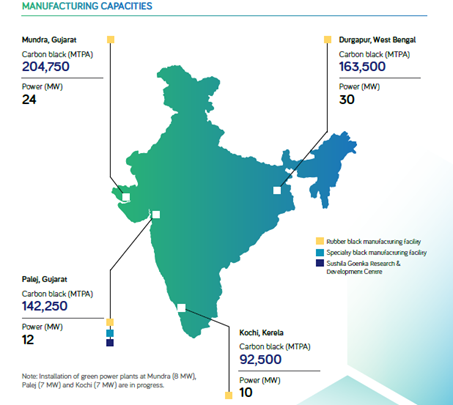
Manufacturing Locations and capacity:
The company has a global presence with exports in more than 45 countries and has 6 global offices. Exports constitute around 26% of the revenues.
They are the 7th biggest producer of carbon black in the world and the biggest in India. Their product portfolio consists of 75 different grades of products for tyres, specialty chemicals and performance chemicals.
They are setting up a new plant in Chennai with a capacity of 147k and 24MW green power. The plant is likely to come up in Q3FY23.
Capacity:
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |
| Production Capacity (Tonnes) | 515000 | 571000 | 571000 | 603000 | 603000 |
| Production (Tonnes) | 387000 | 401000 | 403000 | 406000 | 389000 |
| Revenue (Crores) | 2611.271 | 3528.557 | 3243.54 | 2659.52 | 4446.42 |
| Revenue per 000 tonne | 5.07043 | 6.179609 | 5.680455 | 4.410481 | 7.373831 |
| Utilization | 75% | 70% | 71% | 67% | 65% |
| EBITDA (Crores) | 372.8213 | 614.1205 | 459.14 | 506.39 | 621.38 |
| EBITDA Per 000 tonne | 0.72 | 1.08 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 1.03 |
The company also has power capacity of 91 MW though most of which is captively consumed. This power capacity helps the company reduce its power costs. Also, there are 2 expansion plans – brownfield and greenfield expansion which are likely to go live in FY23 and will increase the capacity to 790k tonnes and power capacity of 115 MW. Between both of these, the capex planned is nearly 1000 crores.
Product profile
Tyre and performance chemicals:
Under the brand names ‘Orient Black’ and ‘CarboNext’, this versatile material is used in rubber compounds as reinforcing fillers to optimize the properties of compounded materials to meet the specific performance requirements. The enhancement of rubber properties is mainly facilitated by the physical and chemical characteristics of carbon black covering Aggregate Size Distribution (ASD), structure, particle size (surface area), surface activity and porosity among others.
PCBL offers a comprehensive portfolio spanning multiple grades of carbon black as classified by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standards, alongside customized, high‑performance products to cater to next generation business needs.
PCBL’s furnace grades of carbon black encompasses various series from N100 (super abrasion furnace black) to N700 (semi‑reinforcing furnace black). These are characterized by a diverse range of surface area and structure. By conferring specific requirements to rubber products, this range provides value addition to a wide variety of tyres and high-performance rubber goods. This range is the volume driver in their business.
Tyre and performance chemicals find the following downstream applications under two primary utilities:
Technical and high performance rubber goods
z Conveyor belts
z Construction
z Extrusions and profiles
z Damping elements
z Hoses and ducting
z Power transmission belts (V belts)
z Rubber mats and shoe soles
z Rubber pads and caps
z Anti‑vibration grommets
z Moulded rubber goods
z Seals and gaskets
z Rubber‑to‑metal bonded goods
z Unvulcanised sheets
z Adhesives
z Tubing
Tyres
z Passenger vehicle tyres
z Truck and bus tyres
z Off‑the‑road tyres
z Agricultural tyres
z Forestry tyres
z Two‑wheeler tyres
z Three‑wheeler tyres
z Cycle tyres
z Tyre re‑treading materials
Crude oil is one the major raw materials and hence an increase in crude oil prices may impact margins negatively. The company suggests that most of the contracts are long term with clauses to protect margins.
Clients:
PCBL’s clientele includes global and Indian tyre manufacturing giants such as MRF, CEAT, JK Tyre & Industries, Apollo Tyres, Bridgestone, Goodyear, Michelin, Yokohama, TVS Group, Continental, Toyo, Nexen, Kumho, Contitech, Giti Tyres, Trelleborg, Camso and Petlas among others. Besides, PCBL caters to the specialty black needs of prominent Indian and global companies. 95% of the clients have been doing business with the company for greater than 5 years.
Management:
| Name | Designation | In company since |
| Sanjiv Goenka | Chairman | Promoter |
| Kaushik Mukherjee | Company Secretary | >5 years |
| Kaushik Roy | Managing Director | >5 years |
| Preeti Goenka | Promoter & Non-Executive Director | Promoter |
| Shashwat Goenka | Promoter & Non-Executive Director | Promoter |
| Sabyasachi Bhattacharya | Head – HR and IT | >5 years |
| Vijay Joshi | Chief Operations | 2 years |
| Raj Kumar Gupta | CFO | >5 years |
The total salary of the management team is 24 crores vs a PAT of nearly 426 crores
Shareholding:
Promoter group: 51.4%
8.4% DIIs
31.6% Individuals
8.6% FIIs
DIIs have increased their stake in the last 4 quarters from 6% to 8.4%, FIIs have reduced stake from 9% to 8.6%. There is 0 promoter pledge and promoter holding have increased marginally from 51.38% to 51.41%
Financials – Last 7 quarter results:
| DESCRIPTION (in Crores) | Mar-21 | Jun-21 | Sep-21 | Dec-21 | Mar-22 | Jun-22 | Sep-22 | Dec-22 |
| Total Revenue from Operations | 867 | 1,004 | 1,068 | 1,156 | 1,219 | 1,409 | 1,628 | 1,363 |
| Total Expenditure | 717 | 877 | 919 | 1,026 | 1,122 | 1,260 | 1,483 | 1,248 |
| EBITDA | 180 | 157 | 182 | 165 | 127 | 195 | 184 | 159 |
| Profit after tax | 128 | 104 | 122 | 112 | 88 | 126 | 116 | 97 |
| Diluted EPS | 3.7 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 3.0 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 3.1 | 2.6 |
| Revenue Growth | 16% | 6% | 8% | 5% | 16% | 16% | -16% | |
| Gross Margin | 41% | 33% | 33% | 27% | 26% | 27% | 23% | 23% |
| EBITDA Margin | 21% | 16% | 17% | 14% | 10% | 14% | 11% | 12% |
| PAT Margin | 15% | 10% | 11% | 10% | 7% | 9% | 7% | 7% |
The revenue has grown consistently except the last quarter mainly due to lower realizations and postponing of buying from tyre companies due to lower inventory costs. The management in their conference call expects the demand to bounce back in Q4FY23.
Market Size:
The current market size is $13Billion globally which is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5% to $18B in 2029. The Indian market size around 1100k tons which is expected to grow at 6% CAGR till 2030. PCBL has production of 387k tons of which around 300k tons are consumed within India. PCBL is the biggest player in India with 30% market share.
The Global Carbon Black industry is sustained by economic growth, which boosts growth in infrastructure, construction, automobile, consumer durable goods and so on. Carbon black consumption is predominantly driven by tyres and other rubber goods while its nonrubber application commands a relatively small share. Carbon black used in high-end non-rubber applications is commonly known as ‘Specialty blacks’, which impart specific characteristics such as high-quality pigmentation, UV protection, dispersion, viscosity control and electrical conductivity.
It also finds application in plastics, inks, paints and coatings and batteries used across industries such as automobile, electronics, textiles, construction, packaging etc. Plastics application is the major growth driver accounting for almost two-third of the volume share of the specialty black market. The specialty black segment is dominated by a few global players with access to technologies that enable production of technically sophisticated products for wider applications. The global carbon black industry is concentrated, with 10 players accounting for almost 60% of the global production capacity.
There is significant increase in capacity planned over the next few years across various companies in India. China has been reducing capacity consistently and the higher power costs in Europe has also led to capacity reduction. This both will aid Indian companies garner significant global market share.
One of the key risks for the industry is replacement of carbon black by Silica though there has been various research that the product is not entirely replaceable due to better abrasion efficiency and in turn higher tyre life.
Global Market
The global carbon black market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 4.4% from 138 lakh tonnes in 2022 to 157 lakh tonnes by 2025.
In terms of revenue, the market was valued at USD 17,558 million in 2022 and is expected to reach USD 22,890 million by 2027, registering a CAGR of 5.4%.
The major factors driving the growth of the market is largely the tyre and industrial rubber product application segment accounted for the largest share, holding more than 70% of the total market in 2022 & remaining led by specialty segment applications like plastics, Toners & printing inks, coating, textile fibres & others.
Largest Players
| Top 10 global carbon black manufacturing companies market share as of FY22 | |
| Particulars | % Market Share |
| Cabot Corporation (US) | 14% |
| Birla Carbon (India) | 12% |
| Orion Engineered Carbons (US) | 9% |
| Jiangxi Black Cat Carbon Black (China) | 6% |
| Tokai Carbon (Japan) | 5% |
| CSRC Group (Taiwan) | 3% |
| Phillips Carbon Black (India) | 3% |
| Longxing Chemical Group (China) | 3% |
| Omsk Carbon Group (Russia) | 2% |
| OCI Corporation (Korea) | 2% |
| Total | 60% |
Capacity and Demand scenario
Global carbon black demand totalled ~15 million tons in 2022, a growth of ~7% from 2021. Carbon black demand is forecast to grow ~4% per year from CY21-25E to reach 16.7 million tons in CY25E. The primary driver of the growth would be the new demand from the tyre industry, based upon $20 billion in new investments that will be spent on new tire production capacity worldwide from 2020 to 2025. The global carbon black industry is concentrated, with 10 players accounting for almost 60% of the global production capacity.
| Particulars | CY18 | CY19 | CY20 | CY21 | CY22E | CY23E | CY24E | CY25E |
| Carbon Black Capacity Globally in lakhs tonnes | 171 | 173 | 176 | 182 | 185 | 190 | 192 | 196 |
| Carbon Black Utilization | 78% | 76% | 69% | 74% | 75% | 77% | 78% | 80% |
| Carbon Black Production in lakhs tonnes | 133 | 131 | 121 | 136 | 138 | 145 | 150 | 157 |
| Carbon Black demand globally in lakhs tonnes | 136 | 134 | 125 | 138 | 148 | 154 | 161 | 167 |
About 93% of global carbon black demand related to its use as a reinforcing filler in rubber, so the fortunes of the carbon black market are linked with the rubber and tyre industries.
Worldwide, about 46 parts of carbon black are consumed for every 100 parts of rubber. In addition to the total volume of rubber used worldwide, carbon black demand is affected by the product mix of the rubber industry, particularly the percentage of rubber used in tyre applications versus non-tyre applications. This is because tyre compounds on average require higher carbon black loadings than non-tyre rubber goods.
An average tyre contains around 3 kg of carbon black, which is roughly 20-25% weight by volume in a car tyre, hence tyre manufacturers consumes the carbon black in bulk. World’s second largest supplier of carbon black is Russia. Manufacturers throughout Europe and the world rely on Russian carbon black since they have large amount of feedstock available. A survey states, around 54% of Europe’s carbon black supply comes from Russia.

Specialty carbon black
Specialty carbon blacks are produced through the partial combustion of hydrocarbons to meet rigorous specifications and deliver important functionality according to end-user performance requirements. These properties of carbon black enable its unique characteristics that deliver critical value to end-users through a range of functionalities including colour, UV protection and conductivity.
Applications of specialty grade carbon black
Specialty grade applications are only to non-rubber applications like plastics, paints and coatings, inks and toners, battery applications etc. which has shown resilience in demand over the past few years.
Plastics industry is the largest end-user industry for specialty carbon black, where it is used to impart colour, improve thermal insulation and impart UV resistance to plastic products such as pipes, engineering plastics, cables and synthetic fibres. In automotive sector, specialty carbon black is used to provide aesthetic appeal to vehicles, improve durability of components and provide protection against corrosion.
Power cables are one of the most demanding applications for specialty carbon blacks as they provide critical performance in semicon shields.
In automotive sector, specialty carbon black is used to provide aesthetic appeal to vehicles, improve durability of components and provide protection against corrosion.
Key drivers of specialty black demand include consumer spending on both durables and non-durables, construction activity and automotive builds and the servicing of vehicles in use. Specialty markets account for only 7% of the carbon black industry’s volumes but 11% of market value due to the higher average prices typical for pigment grades
The largest single market for carbon black outside the rubber industry is plastics, which accounts for about 70% of volume demand for special blacks. Major applications for specialty blacks in the plastics industry are film, blow moulding and injection moulding, wire and cable jacketing, pipe, engineering plastics, fibre and conductive plastics and ESD (electrostatic discharge). In plastics, carbon black is used as a colorant and to improve properties such as UV resistance and electrical conductivity.
Printing inks, paints & coatings together accounts for another 16% of specialty blacks demand. The inks market is diverse, encompassing a mix of commodity (newspaper ink) and high value (inkjet colorants) applications. Paints and coatings market is very small market, totalling just 36 KT in 2020, though it’s a highly challenging and high value market.
The specialty carbon black business has grown much faster than normal grade carbon black with CAGR of 33% vs 3% for normal grade over FY17-22.
Currently, the company has 72,000 tonnes capacity which is operating at 50% utilization levels which is ~7% of overall volumes share in FY23. Considering the robust growth from key end user industries likes plastics and increasing battery applications, the company is expanding by 40,000 tonnes in two phases of 20,000 tonnes each. The first phase is expected to commission by Q4FY23 & second phase is expected to commission by Q4FY24.
The capex on specialty grade carbon black is Rs3bn for 40,000 tonnes which implies per ton cost of Rs80 per kg which is roughly 40% premium than normal grade carbon black.
Post expansion, the specialty grade volumes is expected to ramp up to ~10% by FY25E and still has the potential to reach 15% in the next 4-5 years beyond FY25E. Also, the revenue is expected to grow by 21% CAGR over FY22-25E. Specialty grade carbon black would be a growth compounder for the next 7-8 years.
Current Global Specialty Carbon Black market is estimated to be around 8.7Lakh MTPA in volume terms. It is estimated to grow at 8% CAGR to 11.58Lakh MTPA by FY25.
Globally not many players are known to manufacture specialty black. The market is fairly consolidated with top 3 manufacturers like Cabot Corp, Birla Carbon and Orion Carbon constituting ~60% global market share. In Indian domestic market, PCBL and Himadri specialty have capacities for the same in which PCBL is expanding very aggressively to be at the forefront in providing value proposition to its clients.
The main benefit in specialty CB lies in its quality, which is used for specific purpose application. The input output spreads in specialty CB is almost 2-2.5x of normal grade and enjoys 25-30% margin on average basis as compared with 12-15% on normal grade CB.
Key strengths of the company
The core strength of the company is its 60 years of rich experience in carbon black manufacturing which helps in attracting new clients and retaining its existing clients. The company exports to ~40 countries and have developed very strong relationships with its export’s counterparts. Earlier the company used to sell on spot basis in the export market but then PCBL has strategically realigned its strategy and nurtured its relationship with international Tire companies. Currently, the company enters into long term agreements having fixed volume offtake and also increasing its wallet share with existing clients.
Company’s plants are strategically located with close proximity to ports leading to easy access to raw materials and international customers. It also leads to lower logistics cost as manufacturing facilities are well spread across India & close to Tire Manufacturers.
The company has power generation capacity of 91MW. The company is also consuming in-house its power requirements and remaining is sold after its captive consumption is fulfilled. The company part of the power is sold to the group company CESC Ltd.
The company also enters into medium term agreements for the power offtake. Power business is margin accretive and it adds EBITDA per ton above the carbon black business. The company’s research and innovation centers in India and Belgium have led the company to expand its product portfolio, as well as undertake process innovations to cater to the evolving needs of customer.
The company’s R&D and innovation division has helped the company to develop a strong foundation for customized offerings and innovative solutions for customers. The company is confident & planning of developing 6-7 new grades over the period of two-three years with focus on developing the highest value chain of Specialty products. Additionally, Company has seamless ability to switch between alternative feedstocks.
Economics of the business
| Particulars | FY23 |
| Sales Volume (in MT) | 4,45,184 |
| Revenue Per tonne | 1,29,699 |
| Gross Profit per tonne | 31,933 |
| EBITDA per tonne | 16,061 |
| Capex cost per tonne | 64,626 |
| ROCE | 15% |
Set up cost for a 1 MTPA plant
The company is setting up 1.47lakh MTPA of carbon black capacity in Chennai at a cost of Rs.950 crores which translates to around Rs64,200/MTPA. Also, Co is undergoing a brownfield capex at its Mundra plant for Specialty Carbon Black at a cost of Rs.320 crores which is around Rs.80,000/MTPA.
PCBL’s Revenue have grown at a CAGR of 10% from Rs.2,277crs in FY14 to Rs.5,774crs in FY23
| Particulars | FY15 | FY16 | FY17 | FY18 | FY19 | FY20 | FY21 | FY22 | FY23 |
| Revenue | 2,470 | 1,894 | 1,927 | 2,558 | 3,529 | 3,244 | 2,660 | 4,446 | 5,774 |
| Rev Growth % | -23% | 2% | 33% | 38% | -8% | -18% | 67% | 30% | |
| EBITDA | 151 | 144 | 239 | 373 | 614 | 459 | 506 | 621 | 715 |
| EBITDA Margin | 6% | 8% | 12% | 15% | 17% | 14% | 19% | 14% | 12% |
| ROCE | 12% | 8% | 14% | 19% | 26% | 15% | 16% | 17% | 15% |
| Net Assets | 820 | 1,416 | 1,383 | 1,395 | 1,496 | 1,635 | 1,712 | 1,903 | 1,934 |
Impact of China on carbon black
45% of the World’s Carbon Black used to be in China. Top 2 players in China control 20-25% production. Carbon Black is a polluting chemical so stringent manufacturing processes & protocols need to be followed.
Hence, a lot of small players shut down capacity & market consolidation happened in the industry.
India had imposed anti-dumping duty on China’s imported pneumatic radial tires, hence exports of Chinese tires went down in recent years, while India’s exports increased during the same period.
Carbon Black Feedstock & CBO are the main raw materials required in Carbon Black manufacturing. CBO is a residue which is obtained during steelmaking using Blast Furnace method. China has shut down many Blast Furnace capacities in recent years due to China’s crackdown on pollution. Hence, CBFS & CBO prices have been rising due to is decreasing availability. This along with US China trade war is a structural disadvantage for Chinese players as world is looking at China alternatives & they lose their competitive advantage on cost.
Battery production and importance of specialty black in there
Lithium ion battery formulation typically consist of three components: an active material, a conductive additive, and a binder. Despite making up less than 5% weight of typical lithium ion battery formulations, the conductive additive is critically important for maximizing the energy density and rate capability of the active materials. Carbon blacks are the most widely used conductive additives because they can produce robust electrical networks in the electrodes. These electrical networks are best achieved by carbon blacks that have a high structure and extensive branching. By coating the active material particles and filling in the interstitial space in the electrode with a conductive carbon black, the kinetics of the intercalation reactions of both the cathode and the anode can be greatly improved.
Conductive carbon black additives can also have a significant impact on the properties of both anode and cathode formulation. In traditional lithium ion battery formulations, where the active material, conductive additive, and binder are mixed into a viscous slurry, the carbon black must be well dispersed in that slurry. High structure carbon blacks demonstrate easier dispersion. The dispersibility of the carbon black can have a profound effect on the viscosity and achievable solids loading of the slurry. Slurries with a higher solids loading use less solvent, which can greatly improve the efficiency of battery production.
Carbon Black Manufacturing process
Carbon black is produced by the reaction of a hydrocarbon fuel such as oil or gas with a limited supply of combustion air at temperatures of 1320 to 1540°C (2400 to 2800°F). The unburned carbon is collected as an extremely fine black fluffy particle, 10 to 500 nanometers (nm) in diameter. The principal uses of carbon black are as a reinforcing agent in rubber compounds (especially tires) and as a black pigment in printing inks, surface coatings, paper, and plastics. Two major processes are presently used in the United States to manufacture carbon black, the oil furnace process and the thermal process. The oil furnace process accounts for about 90 percent of production, and the thermal, about 10 percent.
CBFS in the raw material for manufacture of carbon black, which is used by the tyre industry. A small portion of this product is also used by processors to make various downstream chemicals like Agarbatti Oil, White Oil etc. This is also used for manufacture of Rubber Process Oils. There are two types of CBFS viz. High BMCI type and General type. “BMCI” (Bureau of Mines Co-relation Index) effectively measures the degree yield of Carbon Black. The higher the number, the better the yield of Carbon Black. Sulphur content in CBFS reduces the effect of BMCI value.
Oil Furnace Process
In the oil furnace process (Figure 6.1-1 and Table 6.1-1), an aromatic liquid hydrocarbon feedstock is heated and injected continuously into the combustion zone of a natural gas-fired furnace, where it is decomposed to form carbon black. Primary quench water cools the gases to 500°C (1000°F) to stop the cracking. The exhaust gases entraining the carbon particles are further cooled to about 230°C (450°F) by passage through heat exchangers and direct water sprays. The black is then separated from the gas stream, usually by a fabric filter. A cyclone for primary collection and particle agglomeration may precede the filter. A single collection system often serves several manifolded furnaces. The recovered carbon black is finished to a marketable product by pulverizing and wet pelletizing to increase bulk density. Water from the wet pelletizer is driven off in a gas-fired rotary dryer. Oil or process gas can be used. From 35 to 70 percent of the dryer combustion gas is charged directly to the interior of the dryer, and the remainder acts as an indirect heat source for the dryer. The dried pellets are then conveyed to bulk storage. Process yields range from 35 to 65 percent, depending on the feed composition and the grade of black produced. Furnace designs and operating conditions determine the particle size and the other physical and chemical properties of the black. Generally, yields are highest for large particle blacks and lowest for small particle blacks.


