The geospatial industry is rapidly emerging as a key component of both India’s and the global economy, driven by innovations in digital technology, policy reforms, and increasing demand for location-based services. At its core, geospatial technology involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data that has a geographic or spatial component, transforming complex information into actionable insights for decision-making across a wide range of industries. The global and Indian geospatial industries are evolving simultaneously but with distinct characteristics and growth drivers.
Global Geospatial Industry Overview
The global geospatial industry is witnessing accelerated growth, driven by advancements in satellite imaging, Geographic Information Systems (GIS), mobile mapping, and the integration of geospatial data with emerging technologies such as AI (Artificial Intelligence), Machine Learning (ML), cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Global Market Size & Growth:
- The global mobile mapping market was valued at USD 31.78 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16.4% from 2024 to 2030.
- The rapid adoption of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) for environmental monitoring, disaster response, and urban planning is fueling demand for geospatial data, particularly in transportation, construction, and public safety sectors.
- The integration of 5G technology with geospatial systems is further driving innovation by enabling faster data collection, real-time analytics, and enhanced accuracy in mobile mapping and location services.
- Key Applications:
- Environmental Monitoring: Global geospatial technologies play a crucial role in tracking climate change, deforestation, and natural resource management. Advanced satellite imaging and remote sensing help governments and organizations monitor ecological changes in real time.
- Disaster Management: Geospatial systems are essential in disaster response and recovery, providing real-time mapping for earthquakes, floods, and other natural disasters. GNSS systems are widely used for rescue operations, evacuation planning, and damage assessment.
- Urban Planning and Smart Cities: Globally, cities are increasingly utilizing geospatial tools to optimize urban planning, traffic management, and infrastructure development. This is particularly evident in smart city projects in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia, where 3D mapping and geospatial analytics are essential for resource allocation and sustainability.
- Technological Drivers:
- AI & ML Integration: AI and machine learning are transforming geospatial analytics by automating data processing, identifying patterns in large datasets, and making predictive models more accurate. These technologies are helping governments and businesses make faster and more informed decisions.
- IoT & Big Data: IoT-enabled devices are generating enormous amounts of spatial data. Coupled with big data analytics, geospatial systems now offer more precise insights into consumer behavior, traffic flows, and resource management.
Indian Geospatial Industry Overview
India’s geospatial sector is evolving rapidly, supported by government initiatives, liberalized policies, and a surge in demand for location-based services across both traditional and emerging industries. The country’s focus on digital transformation and the strategic importance of geospatial data in large-scale national projects are key factors driving growth.
- Market Size & Growth Projections:
- India’s domestic geospatial market is expected to reach INR 1 lakh crore (USD 12 billion) by 2030, growing substantially due to advancements in technology and government support.
- The Indian Geospatial Analytics market, valued at USD 1.38 billion in 2024, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.82% to reach USD 2.70 billion by 2029. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of geospatial technologies in sectors like agriculture, urban development, logistics, and disaster management.
- Geospatial exports from India are also growing, with estimates that exports of geospatial services will rise to approximately INR 13,100 crore by 2025. This is being driven by innovations, government projects, FDI, and technology mandates.
- Government Policies & Investments:
- India has implemented several significant policy reforms, notably the Geospatial Data Guidelines 2021 and the National Geospatial Policy 2022, which have liberalized access to geospatial data, allowing private companies and government agencies to freely use such data for commercial and developmental purposes.
- Government investment in projects like SVAMITVA (Survey of Villages and Mapping with Improvised Technology in Village Areas), PM Gati Shakti, and the National Hydrology Project demonstrates the centrality of geospatial technology to the country’s infrastructure and rural development.
- The 2023-24 Union Budget increased allocations for space technology, applications, and satellite systems by 16%-21.5%, highlighting the growing importance of geospatial technology in national policy.
- Key Sectoral Applications:
- Agriculture: Geospatial technology is critical for optimizing agricultural practices in India. By analyzing factors such as soil health, weather patterns, and water availability, geospatial tools help farmers improve crop yields, reduce costs, and mitigate risks.
- Urban Development & Infrastructure: In India’s urban centers, geospatial technologies are widely used for planning, traffic management, and smart city initiatives. Projects like the Smart Cities Mission and PM Gati Shakti rely on GIS for infrastructure development, transport planning, and utilities management.
- Logistics & Delivery Services: With the rise of e-commerce, geospatial analytics is playing a crucial role in optimizing delivery routes and reducing time in last-mile logistics for companies like Amazon, Swiggy, Zomato, and Domino’s. Accurate mapping and real-time location data are vital for improving efficiency in these sectors.
- Defense and Intelligence: Defense and intelligence agencies are major consumers of geospatial data in India, using it for border security, surveillance, and infrastructure monitoring.
- Technology Integration:
- India is making strides in cloud computing, AI, and machine learning to process and analyze geospatial data more efficiently. These technologies are helping government agencies, businesses, and researchers make more informed decisions based on real-time data.
- Remote sensing and satellite technologies are becoming increasingly important as India expands its space programs, led by agencies like the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). These advancements are boosting the country’s capability in disaster management, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure development.
Key Growth Drivers in India and Globally
- Increased Demand for Location-Based Services (LBS):
- The penetration of smartphones, growth of e-commerce, and the need for real-time traffic management have spurred demand for LBS across India and globally.
- Companies like Google and local map providers are capitalizing on this trend by offering real-time navigation, route optimization, and traffic updates. For example, Google Street View launched in 10 Indian cities, providing high-resolution, location-based imagery.
- Sustainability and Smart Cities:
- Around the world, geospatial technologies are central to smart city planning, helping cities manage resources efficiently, reduce traffic congestion, and promote sustainability.
- In India, the Smart Cities Mission uses geospatial data to plan infrastructure, monitor urban expansion, and optimize energy usage.
- Policy Reforms and Government Support:
- Liberalized geospatial policies in India are setting the stage for rapid expansion of the domestic market. The easing of data restrictions, and the promotion of private sector involvement, are aligning India with global trends of making geospatial data more accessible for public and private use.
Layers of Geo spatial information system
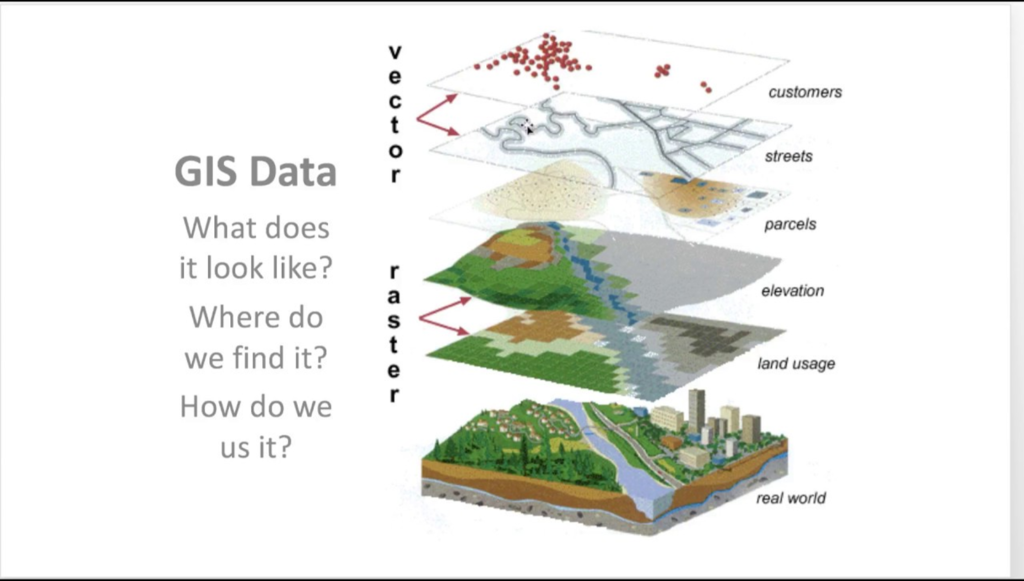
Conclusion
The geospatial industry is evolving into a critical enabler of global and Indian economic growth. Globally, innovations in AI, IoT, and satellite technologies are transforming sectors like urban planning, disaster management, and environmental conservation. In India, government policies, national missions, and growing demand for digital services are propelling the domestic geospatial industry towards substantial growth. With a strong policy foundation, increased technological integration, and expanding applications across multiple industries, both the global and Indian geospatial markets are on track to see remarkable growth over the next decade.


